Introducing a Revolutionary Approach to Virtual Machine Management: Azure Automanage
Simplifying the Complexities for Seamless Control
Are you struggling with the complexities of managing virtual machines in the cloud? Yearning for a more streamlined and efficient solution? Look no further. Welcome to a new era of virtual machine management with Azure Automanage.
In the quest for better control and enhanced efficiency over your cloud-based virtual machines, Azure Automanage emerges as the ultimate tool. With the power to customize configurations, select regions, and simplify processes, this tool is a game-changer.
Stay ahead in the cloud game with Azure Automanage – your key to effortless virtual machine management.
What is Azure Automanage?
Azure Automanage is a groundbreaking cloud management tool offered by Microsoft, designed to simplify and streamline the management of virtual machines (VMs) within the Azure cloud environment. With the goal of reducing complexity and enhancing operational efficiency, Azure Automanage automates various aspects of VM management, including configuration, updates, monitoring, and more.
At its core, Azure Automanage provides users with a centralized and automated way to manage the lifecycle of VMs, ensuring they are consistently configured according to best practices, up-to-date with the latest patches, and monitored for optimal performance. This tool is particularly valuable for organizations seeking to maximize uptime, minimize costs, and reduce the burden of manual management tasks.
Key features of Azure Automanage include:
- Configuration Automation: Azure Automanage helps configure VMs according to Azure best practices. It automatically sets up services, updates, and configurations, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Update Management: The tool automates the process of installing updates and patches on VMs without requiring manual rebooting, ensuring security and stability.
- Continuous Monitoring: Azure Automanage monitors VMs throughout their lifecycle, identifying any configuration drift that may lead to security risks or compliance issues.
- Customization: While adhering to best practices, the tool allows for customization of configurations based on specific requirements, providing flexibility without compromising on standards.
- Centralized Control: Users can manage multiple VMs across different subscriptions and regions from a single interface, streamlining administrative tasks.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Azure Automanage offers integration with Azure Backup, providing reliable backup and disaster recovery options for VMs.
- Resource Optimization: By automating routine tasks, Azure Automanage helps optimize resource utilization, leading to potential cost savings and improved efficiency.
- Security Enhancement: The tool ensures that VMs are consistently configured to meet security baselines, protecting against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Microsoft is likely to introduce 20+ services for automanage. You can customize the configuration preferences, name it, select region, deselect Microsoft antimalware, and backup. These customized preferences can be selected while creating a new VM. Or can be created for an existing one. Selecting the Azure machine best practices or customized preferences speeds up onboarding.
Prerequisites for Azure Automanage:
- Supports Windows Server versions 2012/R2, 2016,2019, and 2019 Azure Edition
- Linux distributions and versions CentOS 7.3+, 8; RHEL 7.4+, 8; Ubuntu 16.04 and 18.04; SLES 12 (SP3-SP5 only)
- Automanage VMs in supported regions West & North Europe, East/West/Central US, West/South Central US, Canada Central, Japan East, UK South, Australia East/AU Southeast and Southeast Asia
- Necessary Role-based access control (RBAC) permissions for new VMs to automanage. (owner, contributor, and user access administrator)
What can you expect from Azure Automanage?
This tool helps you improve workload uptime and reduce costs by automating Windows server. Managing servers in the cloud to scale up operations and reduce complexities. It monitors the complete lifecycle of default environments of development, testing, and production. Detects the drift from purpose and rectifies it. Flexibility to enable/disable selected and new existing virtual machines. Azure storage and networking features will add to the costs of automanage.
Automanage Windows Server:
You can automanage once you create a new or select existing unmanaged VMs Windows Server on the Azure portal.
- Automatic onboarding and configuration
- Install updates without rebooting the virtual machines
- Minimizes the impact of workload with continuous availability
- Effective management of VMs with Azure VM Insights Monitoring
You can use Azure Resource Manager (ARM) to deploy automanage in the Azure portal.
How to Use Azure Policy to set Automanage?
It enables automanage on VMs using DeployIfNotExists of Azure Policy. It is to onboard automanage best practices of virtual machines to all the eligible VMs.
Applying the policy:
- Check the policy definition, to view click on the Assign button
- Stipulate the parameters for Automanage account, profile configuration, and DeployIfNotExists effect
Automanage Account:
It is the identity used by automanage services to perform the automated operations. It is advisable to select these options if you want to automate the allocation of the resources. You can define an identity for more than one administrator appointed purposefully. Also, can create the Automanage account and manage manually or enable Azure VM best practices from the advanced options.
You may opt to use the same automanage account for machines across several subscriptions. The contributor gets access to the role in all the subscriptions. Define the owner, contributor, and administrator roles for better management of virtual machines. To enable Automanage a preexisting Automanage account requires to assign the contributor role on the resource group that contains the VMs.
Enable Azure Automanage for VMs:
If you click select machines as standard practice it will display the eligible machines. To view both eligible and ineligible machines just click the checkbox, this helps pre-assessment. You can also find out the reason for its ineligibility e.g., unsupported region.
Automanage is by default disabled and allows you to choose Dev/test or Production. It gives better control over service selection.
Disable Azure Automanage for VMs:
For the VMs that no longer need to be auto-managed or for manual management just deselect the checkbox beside the VM. View and manage from the list available of auto-managed VMs visible from Automanage- Azure virtual machine best practices option.
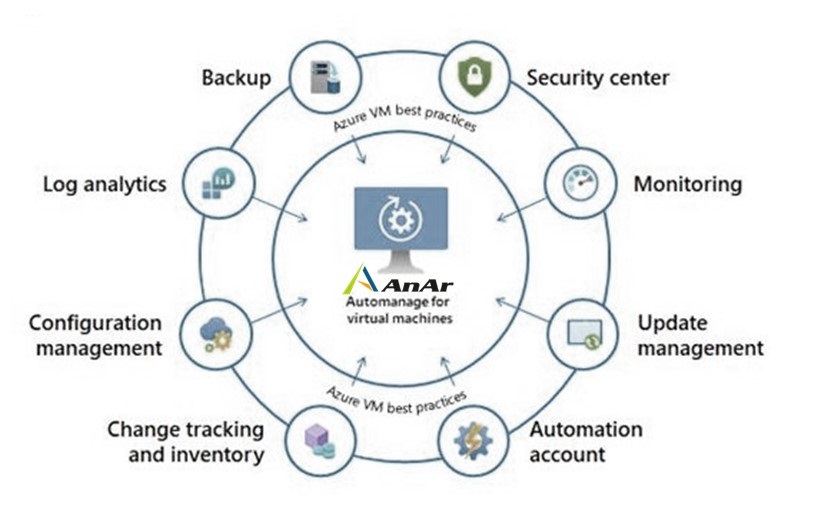
Azure Automanage Best Practices for Windows Server & Linux:
It configures each service as per Azure best practices. The tool supports Azure services and its automation for VMs (virtual machines).
- VM Inventory
- Desired state configuration
- Guest configuration
- Update management
- Tracking change
- Automation accounts
- VM Insights monitoring (not for Dev/Test)
- Azure Backup (not for Dev/Test)
- Log analytics
Automanage is advantageous as it automatically configures the guest operating system as per baseline configurations of Microsoft. Change tracking is flawless when it comes to monitoring virtual machines. It identifies the configuration drift that can lead to the risks of security and compliances.
Azure provides isolated backup for workloads in the production. Integrating the VMs is eased with the recommended settings by automanage. This is useful as best practices for each Azure service are unique. E.g., For Azure backup, the best practice can be backup of the virtual machine on daily basis and the backup retention period set to 6 months. You need to revise the settings based on your requirements. The backup of the Dev/Test machine being a temporary VM thus you save storage fees as by default the backup option is not in the list of services for Dev/Test.
The Azure Security Center enhances the security of data centers and protects them from potential threats across the workloads in the cloud. Microsoft Antimalware lets you have security baselines for the desired state configuration and guest configuration both on the Windows server. For Linux, VMs auto-remediation is not available but allows audit for security baseline via guest configuration.
Information you get on Automanage-Azure machine best practices:
- Name of virtual machine
- Resource Type
- Environment e.g., Dev/Test or Production
- Configuration preferences selected by you e.g., custom preference or Azure Best Practices
- Status whether configured or pending
- Type of Operating system i.e., Windows or Linux (version not mentioned for windows server)
- Account details and Subscription
What are Benefits of Azure Automanage:
- Automatic server management
- Onboards to select best practices of Azure services
- Automatic configuration of each Azure service
- Changes baseline configuration with each version of Windows Server
- Automation of monotonous and time-consuming tasks
- Reduces cost of server management
- Automated operations for the entire lifecycle of the VMs in dev/test/prod
- Optimize and streamline the Windows/Linux Server operations
- Ensures operational security against growing threats
- Improved consistency and uptime
- Keeping pace with cloud innovation
- Assurance of best practices applied to all VMs across the organization
- Easily manage multiple virtual machines running on Azure
- Monitor the VMs throughout the lifecycle
- Automatic detection of configuration drift
- Remediate any configuration drift that occurs in the environment
- Regularly and automatically updated virtual machines
- Protect and restore the backup
- Set backup frequency, even time zone, or switch off.
- Disaster recovery
- Policy Management
- Reliable automation
- Saves time, money, and efforts
Implementing Azure Automanage upholds Windows and Linux VMs to run in their best capacity. The public preview release has received a tremendous response. Overall, it attends to major queries of dependability, security, and management of virtual machines. Increased uptime, operations optimization, and reduced human efforts with many other key features provide error-free management of servers.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Azure Automanage emerges as a transformative solution in the realm of cloud-based virtual machine management. By automating complex configurations, updates, and monitoring tasks, it not only simplifies operations but also enhances security and optimizes resource utilization. With its centralized control, customization options, and integration with various Azure services, Azure Automanage offers a streamlined approach to ensure consistent performance and compliance. As organizations strive to excel in the dynamic cloud landscape, Azure Automanage stands as a key tool to achieve effortless and efficient virtual machine management.