Lean Product Development is the need of the hour where businesses face fierce competition. The pressure to innovate and deliver the solutions to market is enormous. The product development phase is challenging today in a different way that it was after World War 2. Around 1950`s when Toyota developed this concept of “Lean” it would have been difficult to believe that it will define success for every product. Complexities are barriers to good product development, encourages us to take a different path. That diverse path is Lean Product Development.
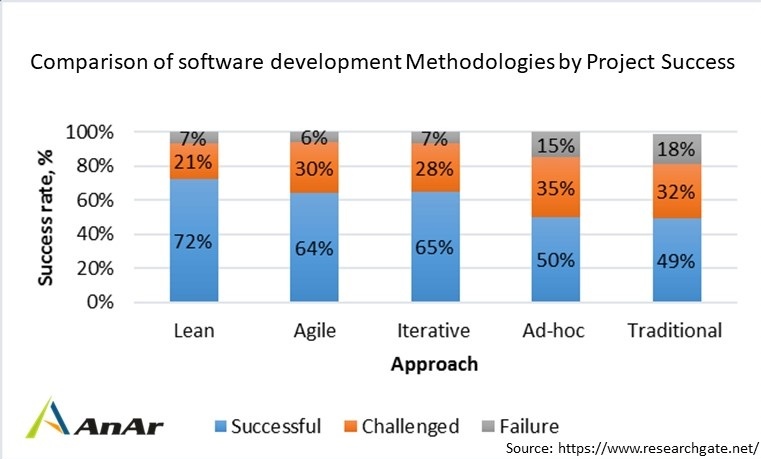
The success rate with various approaches:
- Traditional software development – 49%
- Adhoc -50%
- Agile -64%
- Iterative – 65%
- Lean – 72%
Why do we need Lean Principles in Product Development?
The benefits say it all.
- Optimization of resources
- Elimination of wasted efforts
- Unlimited flexibility
- Improved Visibility
- Better co-ordination
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness
- Reduced time of development cycle completion
- Lesser multiple redevelopment cycles
- Cross-functional teams
- Building reusable knowledge and systems
- Creating teams of experts
- Enabling visualization
- Meeting market needs for innovation
- Building quality solutions
- Speedy product delivery
- Increased profits with higher return on investment
- Value addition for customers
- Deployment of quality features
- Reduced cost of product development
- Standardization of work
- Smaller batch size, faster release
- Synchronization and multitasking of activities
- Immediate feedback increases speed of development
- Saves you from bloating the system with too many features
Many of the lean processes have focus on production. The basic principles are applied through Lean Product Development and Lean Production.
Major differences between Lean Product Development and Lean Production:
- Manufacturing products with purpose to fit production costs in a set margin, while purpose of product development is introducing new products that change lives of people.
- The realized value can be adjusted in production at higher pace due to immediate feedback from quality check department. The product development is complex as the feedback is received from the customer once the feature is developed and released.
- Decisions in manufacturing are based on best practices of industry where as product development works on prominent practices, prototypes and shorter cycle of experimentation.
This clearly states that the application of Lean is dissimilar in production and product development.
What is leadn product development?
Lean product development is a smart way to make and provide things that focuses on being efficient, making customers happy, and always getting better. It’s like a recipe that comes from a way of making cars that Toyota figured out a long time ago. They found out how to get rid of wasteful steps, make things better, and make sure customers get what they want.
Here are the important ideas behind lean product development:
- Thinking About Customers: It’s really important to understand what customers want and need. This means listening to them, getting their feedback, and really knowing what problems they have.
- Seeing the Steps: Imagine drawing a picture of all the steps it takes to make something and get it to a customer. This helps see where things might be done better or faster.
- Getting Better All the Time: Lean says we should always look for small ways to do things better. Even tiny changes add up to big improvements over time.
- Making What’s Needed: Instead of making a lot of things and hoping someone will buy them, lean makes things when someone asks for them. It’s like cooking exactly the right amount of food for the people who are hungry.
- Right on Time: Lean means making things just when they’re needed, not too early or too late. This helps avoid having too much stuff sitting around.
- No Wasting!: Lean really hates wasting things. This can be making too much, waiting too long, moving around too much, making mistakes, or having too much stuff sitting around.
- Working Together: Lean likes small teams that have different skills. They work together to make sure everything comes together smoothly.
- Seeing What’s Going On: Lean uses pictures and charts to show everyone how things are going. This helps keep track and fix any problems quickly.
- Giving Power to Teams: Lean trusts teams to make decisions and take charge of their work. This makes everyone feel responsible and important.
- Starting with Quality: Lean says that quality should be there from the very beginning. Everyone is in charge of making sure their work is top-notch.
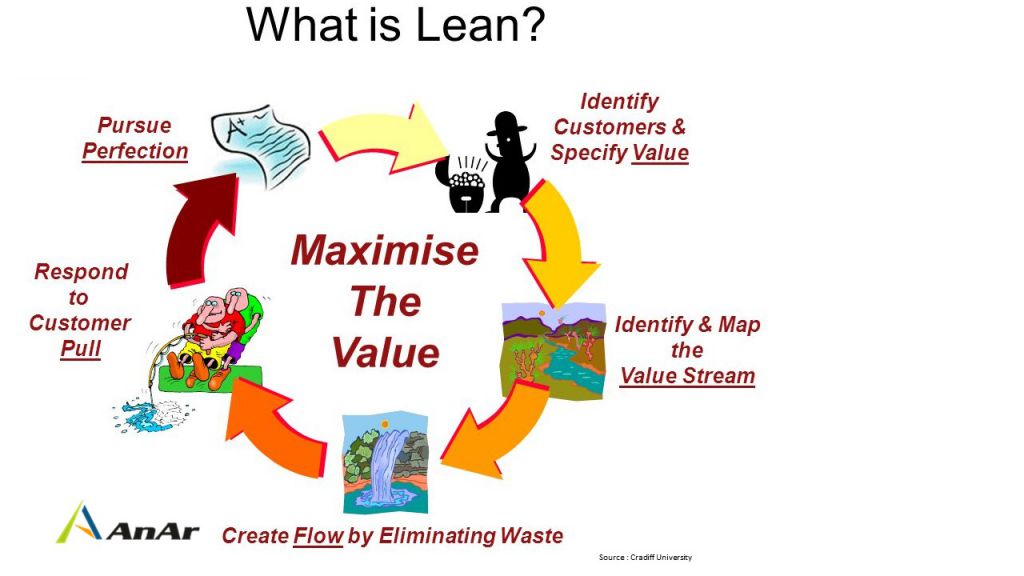
What is the formula for Lean?
Specify Value + Focus on value stream + Create Flow + Pull value + Pursue perfection
Product Development is effective using Lean Principles. Lean Product Development improves workplace efficiency provided you apply the Lean formula accurately. Although principally the lean principles were developed when the car industry faced crisis, its scope covers every industrial and consumer product.
How to develop products effectively using lean principles?
Obtaining effective product development using Lean Principles:
- Specify Value: It focuses on the value your customer draws, requiring you to address what is predominantly important for them. Listening to the voice of customer leads to lean design you need to adapt. To implement the lean development cross functional value addition needs processes.
- Focus on Value Stream: Value stream mapping improves the process of task assignment, revision, discussions, acceptance of a task, actual working on the task, testing and final delivery is continuous, which leads to increase in value-added in fixed time span.
- Create Flow: Value creating process requires to be designed such as it has an uninterrupted flow. Mapping the route to success defines the journey, its planning, challenges, opportunities, and enables product analysis.
- Pull Value: The introduced flow is a guideline that everything is made as demand arises. Behavioral trends can be on peak for a short while so identify the right trend and evolve product around it with specific value for the user. This helps to establish pull by delivering advanced features based on user requirement analysis.
- Pursue Perfection: Ongoing improvement makes the goal achievable and reduces efforts in the process. The key to perfection is smart work with prototyping, testing and revisiting requirements if needed.
Change in the approach that Lean Product Development demands:
- Colossal flexibility in deciding and redesigning the usability quotient of the value
- Train teams to plan their own work, encourage them to work independently and parallelly
- Inculcate the behaviors in order to develop “Lean” culture in any organization.
- Identify the knowledge gap that hampers the product development and recoup
- Ability to adhere to shorter development cycles
- Identifying Value should involve the detailed research, customer expectations, design experts
- Classifying the behavioral trends to benefit product development
- Discovering product that perfectly suits the needs of customers and is not assumptions based
- Decentralized planning reduces pressure and unnecessary discussions
- Save time with standup meetings, prioritization of tasks, and clear communication
- Encourage your team to take decisions based on the historic and research data
- Not letting the past experiences ruin your fresh ideas
- Surveys to contain non-standard questions to encourage users sharing their views
- Every team member should be aligned to the product development with focus on the customer
- Seek perfection to the level it allows you to mange deliverables
- Quality is the best standardization of product but continuous improvement outshines
- Accept the fact that there are things you still don’t know about your customer
- Focus on higher quality for the features that the customer is expecting to work flawlessly
- Have customer centric approach to identify and deal with waste
- Lean principles will speed up work but everything needs its own time for sure
- Continue experimentation using lean principles
Risk of failure applying Lean Product Development:
- Identifying value
- Non static nature of value
- Undefined/underdefined waste categories
- Inflexible approach
- Unidentified knowledge gaps
- Absence of innovative solutions
- No need of new product
- Product development cycle’s inability to deal insecurities
Types of waste you need to deal with in product development:
- Defects
- Delays
- Hand-Offs
- Task Switching
- Over documentation
- Unimportant feature
- Incomplete work
Successful application of Lean Product Development is on whether they are capable to handle unstable conditions.
- People wish for such product – Higher instability
- It is still wanted even with few existing similar products – Moderately instable
- Enough of products prevail, still more products are needed – Quite Stable
Learning first approach is the key to change. Create a powerful team, empower the team applying lean product development specimens and train them for better. A real sense of team work is achieved with lean product development where every team member is working on the product as designed. Idea generation to market entry is a journey that smoothens with lean product development.