What are some of the widely used Cloud Design Patterns?
In the world of cloud applications, cloud design patterns often remain unnoticed until businesses hit a certain scale. As companies grow rapidly, they face both opportunities and challenges. The advantages of increased revenue come hand in hand with heightened technical complexities.
At the heart of this lies a fundamental issue: how to handle application scalability effectively?
Cloud applications come with unique characteristics: they handle unpredictable workloads, rely on standard hardware, and cater to a diverse range of users. These factors bring about specific challenges, including managing configurations, implementing secure authentication, and handling authorization.
Design patterns offer well-established solutions to common software design issues. Instead of providing ready-to-use code, they act as flexible frameworks or guidelines that can be adapted as needed. These patterns offer strategic insights for addressing common challenges across various scenarios.
Cloud design patterns, in particular, are crucial for building reliable, scalable, and secure cloud applications. While we’ll focus on Azure-specific patterns, the principles generally apply to distributed systems on any cloud platform. Before diving into these cloud design patterns, it’s essential to understand the core challenges they are designed to address.
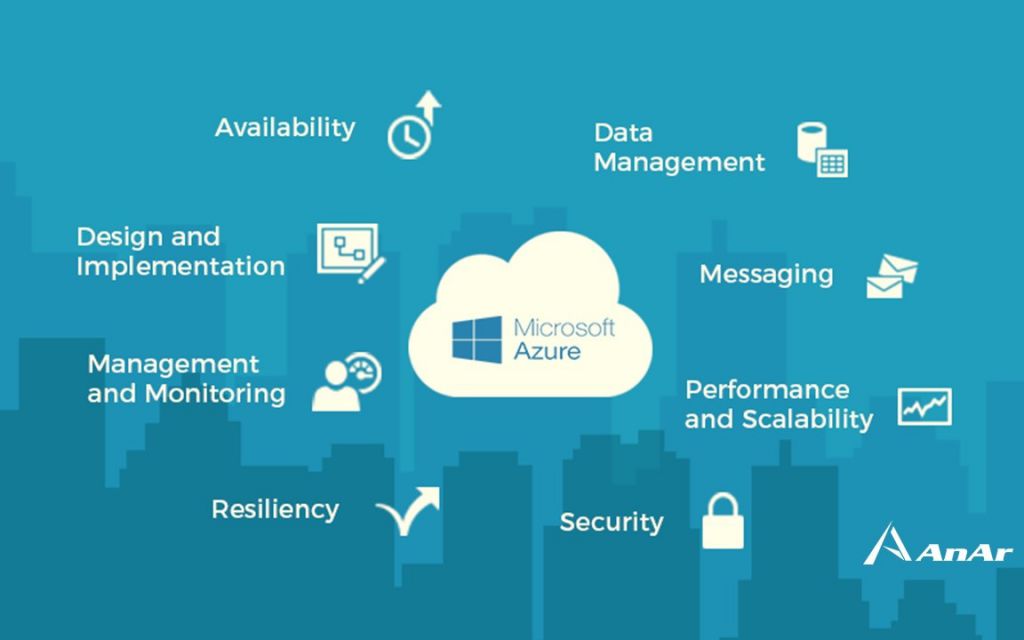
What are the challenges in cloud development?
1.Design Implementation Challenges
Effective design incorporates key principles such as consistency and coherence in component design and deployment. It emphasizes maintainability, making administration and development more efficient, and encourages reusability, allowing components and subsystems to be effectively applied across various applications and environments.
The challenge of choices undertaken throughout the design and implementation stages wields significant influence over both the Caliber and the overall cost of owning cloud hosted applications and services.
2. Data Management Challenges
Data management forms the core of cloud applications, a pivotal factor that shapes most quality attributes. Data is commonly distributed across various sites and multiple servers, driven by considerations such as performance, scalability, and availability. However, this arrangement brings forth a spectrum of challenges. One primary challenge is preserving data consistency, necessitating data synchronization across disparate locations.
3. Performance & Scalability Challenges
Performance refers to how quickly a system responds to actions within a given timeframe, while scalability is the system’s ability to handle increasing loads without sacrificing performance or to easily scale up resources as needed.
Cloud applications often face varying workloads and sudden spikes in activity. Rather than having a fixed capacity, these applications must be able to scale out during peak demand and scale back when demand drops. Scalability challenges go beyond just computation and also include areas like data storage and messaging infrastructure.
4. Security Challenges
Security here means preventing unintended or malicious actions beyond system intent and stopping data loss or exposure. Cloud apps, reachable on the open Internet beyond safe premises, often serve a broad audience, including untrusted users. Ensuring protection from attacks, limiting access to authorized users, and safeguarding sensitive data require careful design and deployment. Solving this challenge requires robust encryption, authentication, and authorization measures. Balancing accessibility with security remains a pivotal concern in cloud application development.
5. Messaging Challenge
Cloud applications’ distributed nature demands a messaging system linking components and services, ideally with loose coupling to enhance scalability. Although asynchronous messaging offers numerous advantages, challenges arise including message sequencing, poison message handling, idempotency, and others.
6. Resiliency Challenge
Building resilient cloud applications presents a unique challenge. Resilience refers to a system’s ability to handle failures smoothly and recover effectively. In the cloud computing environment, where applications often share resources in multi-tenant spaces, rely on common platform services, compete for bandwidth, communicate over the internet, and operate on standard hardware, the likelihood of encountering both temporary and persistent faults increases. Therefore, quickly detecting failures and ensuring efficient recovery are critical to maintaining resilience.
Widely Used Cloud Design Patterns
Below are some of the widely used cloud design patterns in Azure; these patterns apply to any distributed cloud application. Every pattern outlines the issue it tackles and provides insights into the factors to weigh when employing the pattern.
1. Ambassador pattern
Cloud Design Challenge Category: Design Implementation
Create helper services to manage network requests on behalf of a consumer application. An ambassador service acts as an off-site proxy co-located with the client. This pattern offloads tasks like monitoring, logging, routing, security, and resilience in a language-agnostic manner. It’s beneficial for legacy applications or enhancing networking capabilities with specialized teams.
2.Anti-corruption Layer pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Design Implementation
Introduce a façade or adapter layer between disparate subsystems with varying semantics. This intermediary layer converts requests from one subsystem into a format understandable by another. Employ this technique to liberate an application’s design from constraints imposed by external subsystem dependencies. Eric Evans initially outlined this pattern in his work on Domain-Driven Design.
3. Asynchronous Request-Reply Pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Messaging
Unlinks backend processing from a front-facing host, where the backend work needs to happen separately, but the front end still needs a definite response. This cloud pattern proves beneficial in scenarios like client-side code, such as web browser applications, where setting up callback endpoints is tricky or having continuous connections becomes too complicated.
4. Cache-aside Pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Data management and Performance & Scalability
Fetch data as needed into a cache from a data store. This can boost performance and also ensures the cache holds the same data as the underlying data store. This method is useful when the cache lacks built-in read-through and write-through functions or when resource needs are uncertain. This approach empowers applications to fetch data only when required, without assuming beforehand which data will be needed.
5. CQRS Pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Performance & Scalability
CQRS, short for Command and Query Responsibility Segregation, is a technique that divides data store actions into reading and updating functions. Adopting CQRS enhances system adaptability and averts domain-level clashes caused by update commands. This practice is well-suited for collaborative domains where numerous users simultaneously access shared data. With CQRS, you can precisely define commands, curbing potential domain-level conflicts, and any conflicts that do emerge can be reconciled through the command process.
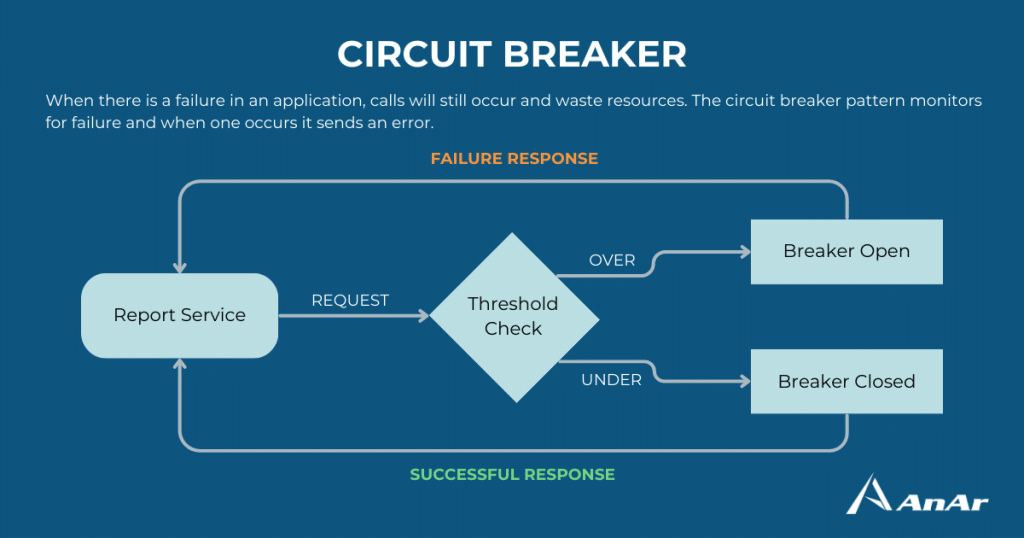
6. Circuit Breaker Pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Resiliency and Stability
Address potential issues that may necessitate varying recovery times when establishing a connection with a distant service or resource. Employing this pattern helps prevent an application from repeatedly attempting to invoke a remote service or access a shared resource if the likelihood of failure is substantial.
7. Queue-Based Load Levelling pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Resiliency, Messaging, Stability, and Performance.
Integrate a buffer queue between a task and the service it triggers. This arrangement helps mitigate occasional intense workloads that might otherwise lead to service failures or task timeouts. By doing so, you can effectively reduce the repercussions of demand surges on the availability and responsiveness of both the task and the service. This technique is beneficial for any application reliant on services susceptible to becoming overwhelmed.
8. Materialized View pattern
Cloud design challenge category: Data management and Performance
Create preconfigured views of data across one or multiple data stores when the existing data isn’t optimally structured for the queries you need. This practice aids in facilitating streamlined data extraction, efficient querying, and overall application performance enhancement. This approach is valuable in scenarios where crafting temporary views can notably elevate query speed or when these views directly function as data sources or transfer objects for UI, reporting, display, or supporting situations where consistent connectivity with the data store isn’t guaranteed. In such cases, caching the view locally becomes a feasible option.
Final Thoughts —
Design patterns provide guidance and offer optimal solutions for the recurring challenges encountered in the design of cloud-hosted applications. However, scaling a cloud based application can prove quite daunting. Frequently, IT teams confront the decision of selecting between a design pattern that accommodates growth for a mere six months and one that caters to expansion over six years.
Based on our experience, options within the six-month timeframe tend to be more cost-effective. Allocating a few weeks to secure a half-year buffer enhances support for business needs and user demands. This approach proves more effective than dedicating an entire year to constructing a sturdier system that’s inherently resistant to change.
A medium-term focus doesn’t equate to short-term shortcuts or makeshift solutions. By diligently integrating common design patterns, an application can be both well-maintained in the long run and adaptable to evolving circumstances.
Our team of cloud computing experts are well equipped with modernizing applications with all of the cloud design patterns, schedule a free consultation or get in touch with us today!