Staying relevant in today’s tech landscape feels like racing against the clock. With software releases happening faster than ever, companies are under pressure to innovate quickly or risk being left behind.
To keep pace, methodologies like design thinking, lean, adaptability, and agile have taken center stage, promising improved collaboration, creativity, and streamlined development.
But here’s the catch: while these approaches are invaluable for rapid ideation and testing, they’re not the entire solution. True, lasting success requires integrating these methods into a larger, carefully balanced innovation strategy.
In this blog, we’ll explore the nuances of design thinking, agile, and lean methodologies and their role in the innovation process. Join us as we navigate the exciting and ever-changing world of innovation and uncover the strategies and tools that can help your company stay ahead of the curve.
How does combining these approaches contribute to team transformation?
To create lasting value and truly transform a team, it’s essential to thoughtfully integrate and align various approaches like design thinking, agile, and lean within a cohesive strategy. This means evaluating key factors—process alignment, organizational structure, resource allocation, and company culture—to ensure a well-rounded and effective implementation.
By harnessing these methodologies, organizations can spark innovation, boost productivity, and enhance business outcomes. However, success hinges on synchronizing every facet of the innovation process, from business models and pricing strategies to supply chains, customer targeting, and marketing—all operating like a well-oiled machine.
When applied thoughtfully, these approaches enhance competitive advantage, elevate customer satisfaction, and drive growth. It’s crucial that any new methods align with the existing company philosophy, seamlessly blending into workflows to ensure profitability and impact. This not only yields meaningful results but also enriches team satisfaction, attracts top talent, and secures a foundation for long-term success.
Planning consideration before running these approaches
Starting a problem-solving process requires a clear grasp of the perspectives and expectations surrounding the issue. Defining the problem space and brainstorming multiple potential solutions through iterative testing is key. Ultimately, the team should plan and execute trials that yield insights for refining the final solution continuously.
For these methods to thrive, a supportive environment is essential. Before diving in, it’s critical to address a few foundational questions to set the stage for impactful, profitable results.
- Are things clear for working together or alone?
- Are the employees under any pressure to deliver it within a time frame?
- Are the employees comfortable sharing their ideas?
- Is the environment for employees under some sort of fear of being bang on all the time?
Ultimately, effective problem-solving and solution-building are about working collaboratively and achieving success as a team. Therefore, it’s necessary to analyze each aspect of the team’s work environment in detail to ensure the highest level of success.
Understanding Approaches
Before proceeding further, it is important to comprehend the dissimilarity between agile, lean, and design thinking. For newcomers to this area, it might be difficult to distinguish between these three methods of continuous deployment and continuous development.
Each approach has its unique audience, constituents, and process.
Design Thinking is the way we identify and resolve problems.
Lean is the framework we use to evaluate our ideas and navigate our way toward the right solutions.
Agile is the method we use to adapt to changing circumstances with software.
These approaches offer different ways to approach problem-solving and can be used in combination or separately, depending on the situation.
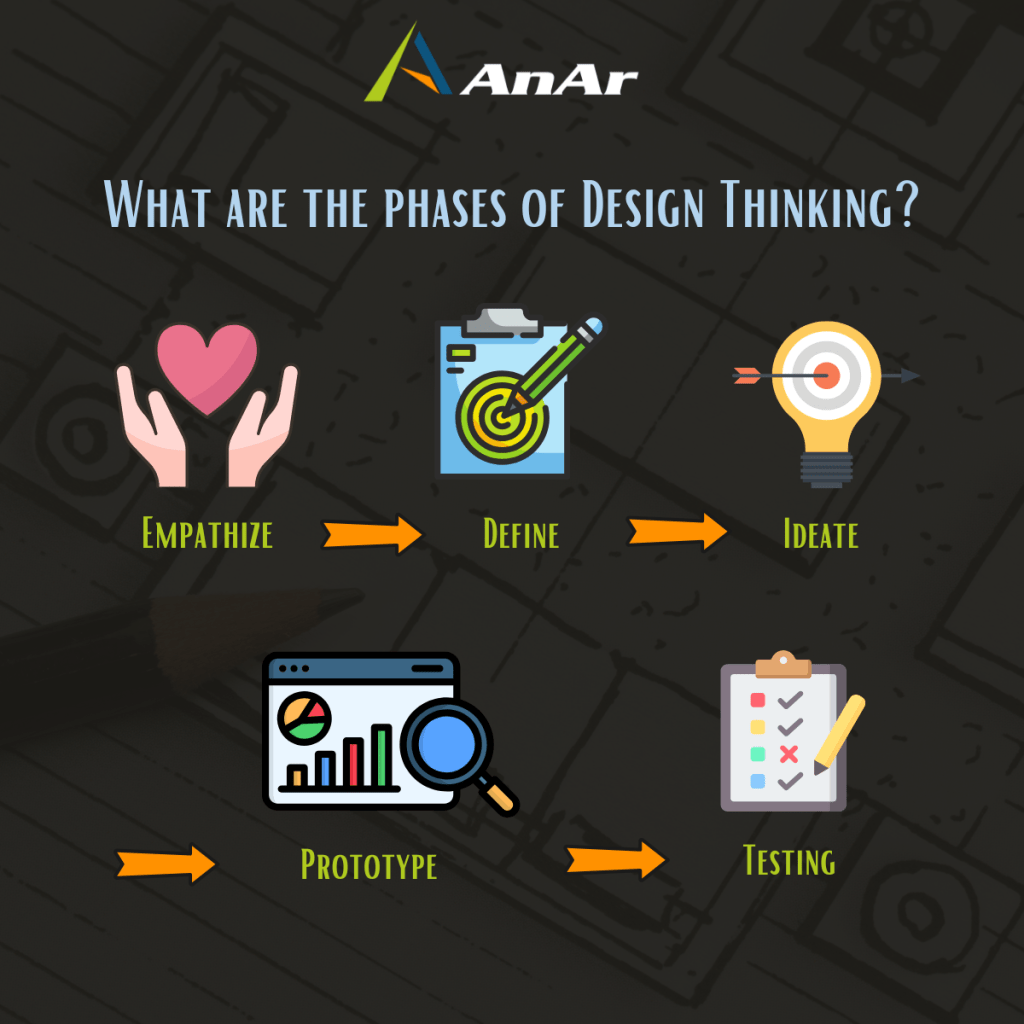
Design Thinking (Identifying)
Design Thinking equips designers with a set of essential skills to navigate uncertainty, merge ideas, and test solutions effectively. This skill set is invaluable for tackling complex problems and generating innovative solutions. The process begins with discovery—an essential phase where designers identify core issues and explore possible solutions, paving the way for new, meaningful concepts.
As a problem-solving framework, Design Thinking empowers individuals and organizations to enhance their ability to develop solutions that meet client and customer needs. With its emphasis on creativity, collaboration, and experimentation, Design Thinking offers a distinctive approach to addressing challenging problems and fostering innovation.
Origin of Design Thinking — Emerging in the 20th century, Design Thinking adapted the industrial-design process for broader problem-solving through a designer’s perspective. By emphasizing empathy with the target audience throughout the process, it proves invaluable for addressing complex, ambiguous problems. Deep user research helps uncover users’ perspectives and test their responses to potential solutions, making it ideal for products and services where usability and customer value are paramount.
Agile (Iterating)
Agile and Lean methodologies are closely related, but they differ in terms of their applications and approaches. Agile is particularly suited to situations where uncertainty is high, as it provides a way to develop software that is adaptable and can evolve over time. Rather than focusing solely on finding the perfect solution, Agile emphasizes the importance of continually improving and iterating on solutions as new information becomes available.
The key characteristic of Agile is its ability to adapt to changing requirements and circumstances in a seamless manner. This enables teams to create software that is robust and can withstand unexpected changes, ultimately leading to greater success and customer satisfaction. By adopting Agile methodologies, teams can not only improve their ability to respond to changing circumstances but also increase their efficiency and productivity, leading to improved business outcomes.
Origin of Agile — The term “Agile” in this context originates from the 2001 Manifesto for Agile Software Development. A group of software developers convened in Utah to propose an alternative to traditional software development, which involved lengthy plans and time horizons. The manifesto drew from emerging methodologies like Scrum and Extreme Programming to hasten the software development process and increase adaptability to change.
Lean Startup (Improving)
Once a solution is identified and ready for implementation, integrating lean thinking into the process becomes essential. Lean thinking isn’t just a toolkit—it’s a mindset that can transform the team’s approach to work. In today’s digital age, where complexity, unpredictability, and constant change are the norms, trying to control every aspect of a project is impractical. Success in this environment depends on clear communication and cohesive teamwork, supported by effective processes, guidelines, and methodologies.
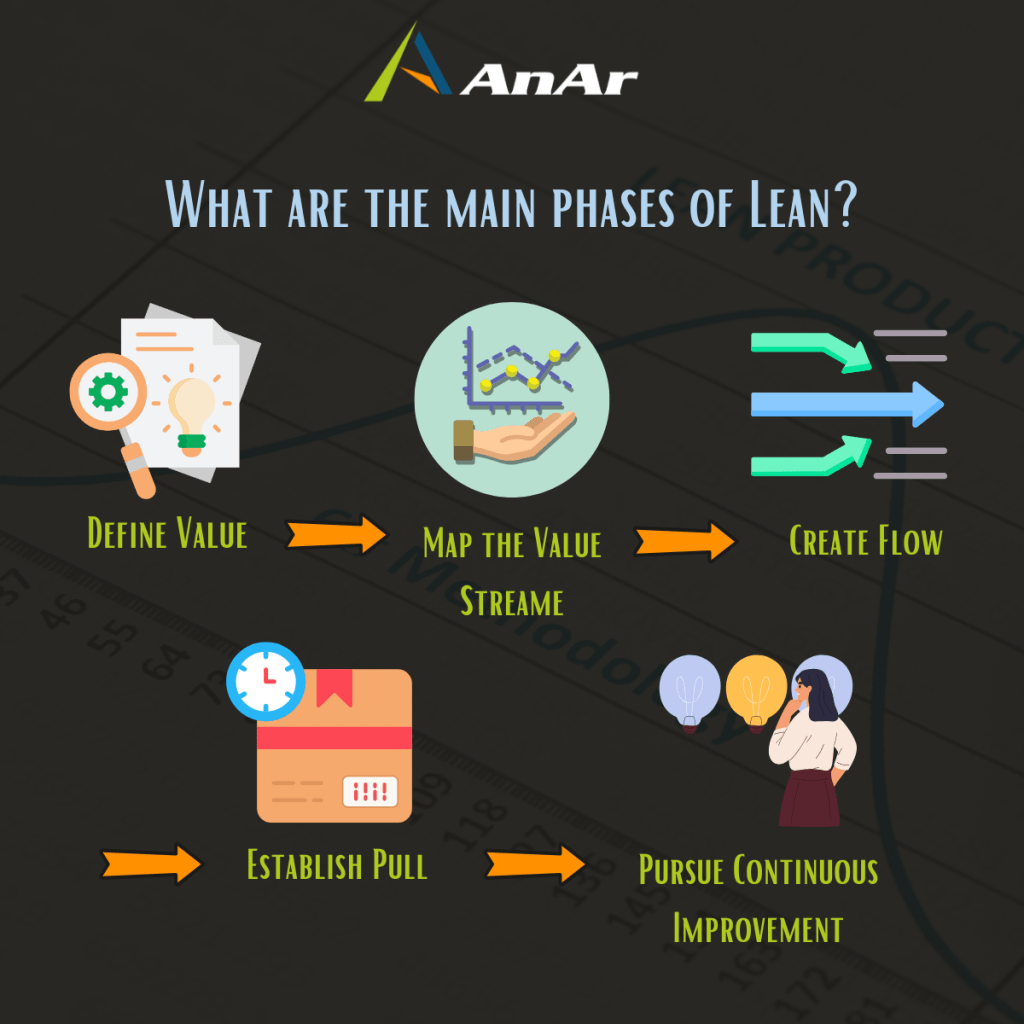
Lean provides a different perspective for managing any kind of work. At its core, Lean is about embracing ambiguity, making decisions through trial and error, and enabling individuals to achieve desired outcomes. Instead of being overly analytical, Lean encourages adaptability and flexibility. By adopting Lean principles, teams can improve their problem-solving abilities, optimize their workflow, and ultimately achieve greater success.
Origin of Lean Startup — “Lean” originated in the 20th century as a way to improve manufacturing and service processes, with Toyota credited as one of the pioneers of its foundational concepts. Instead of increasing scale, Toyota focused on eliminating waste after World War II, developing concepts such as just-in-time inventory and small batches for continuous improvement. The core of Lean is to create an organization where people are empowered to explore better ways of delivering customer-defined value by identifying and removing waste while preserving value.
Together in action
In essence, if you want to generate great ideas, the design thinking approach can be utilized. After that, the lean startup methodology assists in transforming those ideas into functional corporate prototypes. Lastly, the agile methodology helps in delivering the product to the market in a stable and incremental way with the goal of receiving continuous feedback, which can be used to refine and improve the product according to customer needs.
This process can be better understood through the diagram presented below:
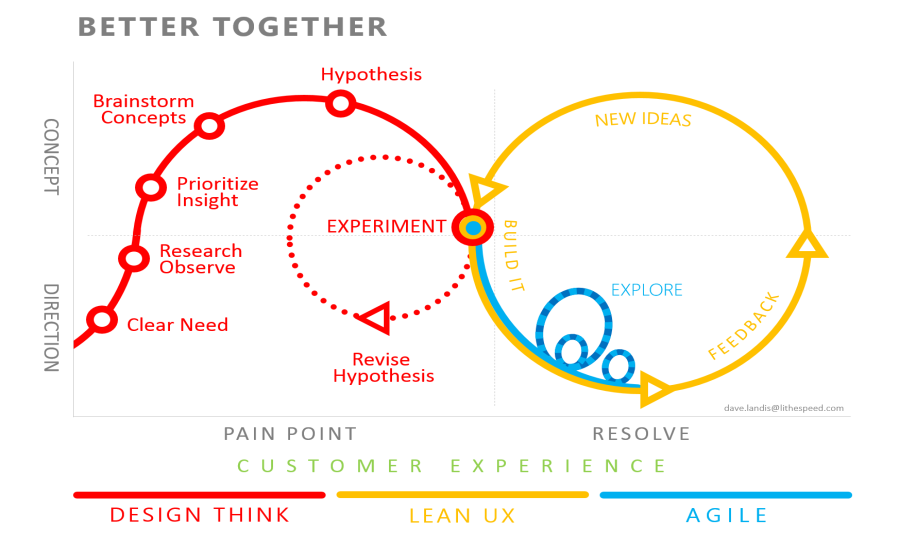


In simpler terms, when we combine design thinking, lean startup, and agile approaches, it helps specialists not only come up with excellent ideas but also turn them into profitable solutions by delivering them in a way that creates immediate value for customers and reduces costs and design errors.
However, it is essential to note that to achieve this, it is important to create a solid and reliable prototype that closely resembles the problem or client request. Each of these approaches has unique concerns and requires different learning strategies. So, it is crucial to choose the right approach that suits the specific situation and then implement it effectively to achieve the desired outcomes.
Conclusion
In essence, the three core approaches in product development—design thinking, lean, and agile—not only empower companies to build better products but also elevate employees’ potential for a more fulfilling work experience. By integrating these approaches and involving every team member in both product discovery and delivery, teams can achieve greater transformation and success. Ultimately, customers care about results, not methodologies—they want a product or service that solves their problems effectively. The focus should remain on seamless process execution, ensuring that each team member understands the workflow and leveraging each approach’s strengths for continuous improvement and rapid software delivery.
All three approaches are vital for meeting the demands of today’s innovative market.