In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the ability to adapt and innovate is not just an advantage—it’s a necessity for survival and growth. As businesses across various sectors seek to harness the power of technology to stay ahead, cloud migration emerges as a pivotal strategy.
But what exactly is cloud migration, and how can it transform your organization’s approach to technology and competitiveness?
Understanding the basics of cloud migration and the various steps involved in making it happen can help you make informed decisions on the best strategy to achieve a smooth transition to the cloud.
This blog will guide you through the intricacies of cloud migration, revealing why it is more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic move that can redefine your business. From small enterprises aiming to boost operational efficiency to large corporations seeking to optimize their technological footprint, understanding the full scope of cloud migration is essential.
 What is cloud migration?
What is cloud migration?
The process of transferring data, applications, or other business components from an organization’s in-house infrastructure to a cloud computing environment is known as cloud migration. This process allows businesses to take advantage of the many benefits cloud computing offers, such as increased scalability, reduced costs, and improved disaster recovery capabilities. By adopting the on-demand, self-service model of the cloud, businesses can achieve end-to-end digital transformation and outmaneuver uncertainty.
Why is cloud migration being rapidly adopted?
As technology continues to evolve, many companies are looking for ways to improve their infrastructures and performance. In recent years, cloud computing has become popular among many companies. This is because companies are finding that their legacy systems, such as aging servers or unreliable firewall appliances, are becoming increasingly inefficient and are no longer operating at their optimal capacity. However, it is essential to note that migrating to the cloud is not a simple process and requires careful analysis, planning, and execution to ensure that the cloud solution is compatible with the business’s specific needs.
When planning a migration to the cloud, it is important to consider not only the process of getting there but also what will be done once the migration is complete. For example, companies need to think about how their applications will be rebuilt so that they can perform optimally in the cloud environment. This process is known as application modernization.
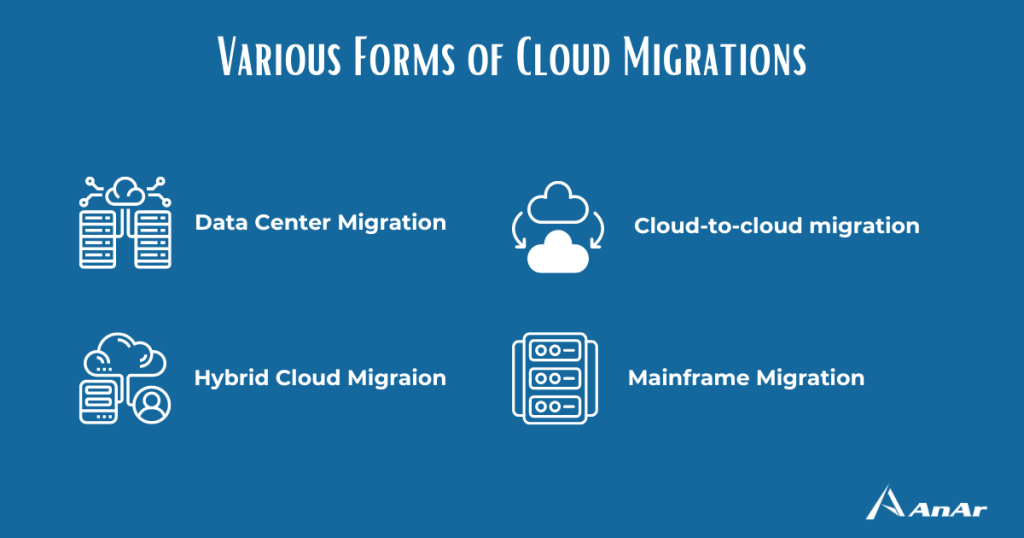
What are the various forms of cloud migration?
When moving resources, such as data and applications, from one place to another, the type of resource and the destination location are crucial considerations in the process. These are known as the “workload” and the “migration destination,” respectively, and play a significant role in determining the success of the migration.
This section will explore various migration scenarios and give a general overview of the procedures, recommended practices, and business-related factors involved in them.
Datacenter migration
Datacenter migration involves relocating data from in-house servers and mainframes, typically located in a company’s office, to servers run by a cloud provider. These cloud-based servers are usually found in large, secure, and professionally maintained facilities. The most common method of moving data center resources to the cloud is through high-capacity networks, but if a strong network is not available, resources can be transferred by dragging them onto high-capacity disks or “data boxes” and physically shipping them to the cloud provider for uploading to their servers.
Hybrid cloud migration
Another common migration scenario is hybrid cloud migration, where organizations opt to keep some of their resources on their on-premises servers and move only a required portion of them to the cloud, creating a “hybrid cloud” environment. This approach allows organizations to make the most of their existing on-premises data center equipment while also meeting industry and government compliance requirements. Additionally, hybrid clouds can also be used for cloud-to-cloud backup, which serves as a disaster recovery solution in case the on-premises data center becomes unavailable.
Cloud-to-cloud migration
Cloud-to-cloud migration is a process in which an organization moves its resources, such as data and applications, from one public cloud to another. This type of migration is becoming increasingly popular as organizations adopt multiple cloud environments, often as a result of mergers and acquisitions. By moving resources between different public clouds, organizations can take advantage of various cloud platforms’ products, services, and pricing and optimize their IT infrastructure for cost and performance. Additionally, a central management tool can be used to manage and monitor resources across multiple clouds from a single location, simplifying the management process. This type of migration is also helpful for organizations that want to implement a disaster recovery solution by having a backup of their data and applications in different clouds.
Application, database, and mainframe migration
Migrating applications, databases, and mainframes is a common practice in the technology industry. Different types of workloads can be migrated, such as Linux, SAP, SQL Server, and Windows Server. Mainframe migration is also quite common, with IBM and Unisys being the most commonly used systems. Moving these workloads to the cloud can offer a variety of benefits, such as lower costs, improved performance and reliability, access to cloud-based developer tools and APIs, more robust security, and the ability to quickly scale up or down without the need for additional equipment. While it is possible to move these workloads without making any changes to them (a process known as “lift and shift” migration), there are advantages to updating or “refactoring” them to optimize their performance and reliability in the cloud environment.
What is the process for cloud migration?
Moving a company’s operations to the cloud is a significant undertaking that requires careful consideration and planning. The process of migrating to the cloud can have a profound impact on a business and its operations, making it essential to have a clear understanding of the steps involved. A comprehensive end-to-end view of the migration journey is necessary to ensure that the necessary capabilities and activities are in place to execute the migration successfully.
The process of cloud migration can be broken down into three main steps: Defining your strategy and building your business case, discovery and assessment, and Cloud migration.
Defining your strategy and building your business case
The initial step in the process of cloud migration is to establish a clear strategy and build a comprehensive business case. This step involves identifying the specific business objectives that the company hopes to achieve by moving to the cloud. It is important to remember that migrating to the cloud is not just a technical exercise, but the desired business outcomes should drive it. Once the objectives are identified, the company can start developing a cloud migration strategy and the business case for the move.
A vital aspect of this strategy is determining which applications will be migrated to the cloud and which type of cloud environment they will be moved to. Also, it is important to have a clear understanding of the infrastructure that will be required to support the migration and how it will look like once the migration is completed. This will help determine the specific steps required to prepare for the migration.
Discovery and assessment
The second step in the process of cloud migration is discovery and assessment. This step is critical in understanding the current state of the business’s IT infrastructure, applications, and data. This is done by conducting a thorough scan and assessment of the existing landscape to identify the current architecture and determine the best applications and data to migrate to the cloud. This includes identifying the different applications that the business currently uses, mapping out the dependencies between them, and assessing the risks associated with migrating them to the cloud based on their current usage. Additionally, it may also include optional pre-migration predictive analysis.
The goal of this step is to enable migration planners to make informed decisions about which applications and data to migrate to the cloud and how to do it in the most efficient and effective way possible. By understanding the current state of the business’s IT infrastructure, applications, and data, migration planners can minimize the risk of migration and ensure that the service level agreements are maintained after the migration is complete. The outcome of this step is the Cloud Migration Assessment, which provides a clear and actionable plan for the migration.
Cloud migration
The final step in the process of cloud migration is the actual migration of the business’s IT infrastructure, applications, and data to the cloud. This step is where the majority of the work takes place and typically involves modernizing existing applications for the cloud, developing new cloud-native applications, and transforming the architecture and infrastructure of the business’s IT systems. This step aims to establish a new technology operating system and work culture that allows the company to advance more rapidly, productively, and efficiently.
Automated management and migration tools are essential for executing a smooth migration. These tools not only speed up the migration process but also ensure that it is done with high quality, consistency, and repeatability. When used in combination with specialized skills and solution accelerators, they can form a “cloud migration factory” that can further accelerate the migration process.
It is also essential to have a robust cloud journey management plan in place to keep the migration effort on track. This plan will help ensure that the migration is completed on time and within budget and that the business’s IT systems are fully operational and meeting the required service level agreements after the migration is complete.



Cloud Migration: The Benefits & Challenges
For organizations that embark on the journey of migrating their operations to the cloud, the transition can result in a significant impact on the business.
The cloud computing model provides a range of benefits, some of which are outlined below:
-
- Increased Scalability: One of the primary benefits of cloud computing is the ability to scale computing resources up or down as needed without significant capital expenditures. This is especially important for companies experiencing rapid growth, as they can quickly accommodate new employees, customers, and data without having to purchase additional hardware.
- Improved Flexibility: With the cloud, companies can access computing resources from anywhere, at any time. This allows them to be more responsive to changing business needs and provides greater flexibility in terms of where and when work is performed.
- Enhanced Security: Cloud service providers invest heavily in security measures to ensure the protection of customer data. By leveraging these investments, companies can benefit from enhanced security without having to make significant investments in their own security infrastructure.
- Lower Costs: With cloud computing, companies only pay for what they use rather than having to make significant upfront investments in hardware and software. This can result in lower overall costs and increased profitability.
- Increased Collaboration: Cloud-based collaboration tools, such as online document storage and shared workspaces, allow teams to work together more effectively and efficiently, regardless of location.
- Compliance: In industries that are highly regulated, such as finance, healthcare, and government, ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations is of utmost importance. To cater to these needs, some cloud service providers offer specialized solutions designed to meet the compliance requirements of these industries.
- Backup, Failover, and Recovery: One of the critical advantages of using cloud computing is the built-in backup, recovery, and failover capabilities offered by most cloud service providers. These features are designed to ensure the availability and accessibility of critical data and systems, even in situations of a disaster or outage. One of the key benefits of these solutions is that they typically offer one-click backup and recovery capabilities, making it easy for organizations to quickly recover lost or damaged data.
- Simplified Monitoring and Management: Another advantage of cloud computing is the simplified management and monitoring that it offers. Many cloud service providers provide centralized management tools that allow organizations to manage and monitor their data centers and cloud resources from a single interface. This centralized management tool offers a comprehensive view of all cloud resources, making it easy for organizations to track resource utilization, monitor system performance, and manage security and compliance policies.
While cloud migration offers many benefits, the process of migrating to the cloud can also present a number of challenges.
Some of the most common migration challenges include:
-
- Complexity: Migrating your existing systems to the cloud can be a complex process involving multiple stages and a variety of different tools and technologies. This complexity can make it difficult for organizations to accurately assess the time and resources required to complete the migration.
- Data security and privacy: Migrating sensitive data to the cloud can raise concerns about data security and privacy. Organizations need to ensure that their data is protected against unauthorized access and that the cloud provider has robust security measures in place.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating cloud-based systems with existing systems can be a complex and time-consuming process. Organizations need to ensure that their existing systems are compatible with the cloud and that data can be easily moved between the two.
- Downtime: Migrating to the cloud can result in temporary downtime for critical systems and applications. This downtime can impact business operations and can be difficult to predict and manage.
- Cost: The cost of migrating to the cloud can be high, including the cost of cloud services, hardware upgrades, and consulting fees. Organizations need to accurately assess the costs involved and ensure that they have the budget to complete the migration.
Final Wrap-up
As we’ve explored in this blog, cloud migration is more than just a technological shift; it is a strategic transformation that can revolutionize how your business operates and competes in the digital age. The journey to the cloud, while complex, offers significant rewards including enhanced scalability, flexibility, security, and cost savings. These benefits can help you not only meet the current demands of your market but also anticipate future challenges.
For organizations ready to embark on this transformative path, it’s essential to approach cloud migration with a well-defined strategy, thorough planning, and a clear understanding of your desired outcomes. Whether enhancing existing applications or deploying new cloud-native solutions, each step should be aligned with your broader business goals to ensure a seamless transition.
At AnAr Solutions, we are committed to guiding businesses through every phase of their cloud migration journey. Our team of experts specializes in both lift-and-shift migrations and sophisticated modernization initiatives. We understand the nuances of cloud technology and are ready to help you leverage its full potential to drive your business forward.
Ready to start your cloud migration journey?
Contact us today to schedule a consultation with our cloud specialists.
Together, we can unlock new opportunities and propel your business towards a future rich with innovation and growth.